Here come the sundials! Prof uncovers eight ‘hidden’ sundials in ancient mosaics
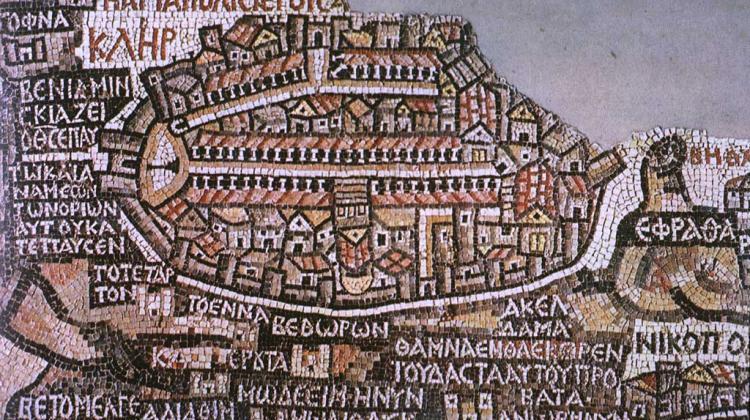 Professor Marek Olszewski noticed a previously unknown depiction of sundial in Madaba Map, a great mosaic located in Jordan. The sundial is located next to the gate on the left. Credit Wikipedia/public domain
Professor Marek Olszewski noticed a previously unknown depiction of sundial in Madaba Map, a great mosaic located in Jordan. The sundial is located next to the gate on the left. Credit Wikipedia/public domain
A university professor studying ancient mosaics has discovered eight previously unknown sundials in the designs, taking the total number known number to 15.
Professor Marek T. Olszewski from the University of Warsaw was re-examining a number of mosaics dating back to the 2nd century AD when he made his startling discovery.
One of the mosaics from the 6th century AD which was discovered by the Gate of Damascus in Jerusalem, Olszewski noticed that between a richly dressed women, a mysterious object is visible, which scientists at the beginning of the 20th century described as an oil lamp or column.
Olszewski said: ”After careful analysis and comparison with a sundial discovered during excavations, I came to the conclusion that this mosaic and other ones similar to it depict sundials.”
Another sundial "tracked" by the Polish researcher is located in a wall mosaic in Santa Cecilia in Trastevere church in Rome. This mosaic was created during the time of Pope Paschal I (817-824).
Prof. Olszewski also noticed a previously unknown sundial in the Madaba Map - a huge floor mosaic, which is currently stored in the church of St. George in Madaba, Jordan. It shows a map of the Middle East from the Byzantine period. This is the oldest cartographic depiction of the Holy Land, including Jerusalem and dates back to the 6th century AD.
Yet another depiction of a sundial comes from Tarsus (Mersin) in Turkey, where a figural mosaic (ca. 2nd-3rd century AD) shows a sundial on a column and a crow sitting on it. A man tries to scare off the bird by throwing a pouch at it (crow was a symbol of a bad omen).
Sundials were often used in ancient times to determine time. They indicated time with a shadow cast by a stationary pointer (gnomon) on a dial with hour markers. They belong to the oldest scientific and measuring instruments. The oldest ones are from ancient Egypt. In the Mediterranean zone in ancient times they were placed in both public and private places.
PAP - Science in Poland, Szymon Zdziebłowski
szz/ zan/ kap/
tr. RL
Przed dodaniem komentarza prosimy o zapoznanie z Regulaminem forum serwisu Nauka w Polsce.