Appreciate bitter taste of tannins
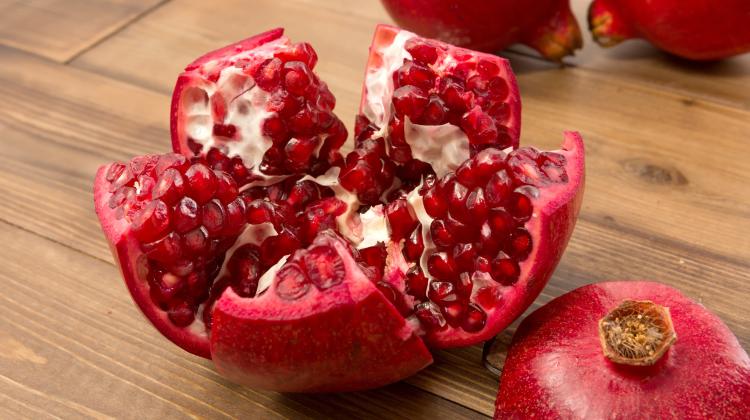

Astringent taste, which we feel when eating ate unripe fruit, is the effect of tannins present in food. The unpleasant taste of tannins protect plants from attacks by herbivores. Tannins also protect people against cancer, slowing down the rate of cancer cell division.
Properties of tannins are under the microscope of researchers at the Institute of Animal Reproduction and Food Research of the Polish Academy of Sciences in Olsztyn. "Tannins are very common in the plant kingdom, so also in foods of plant origin. They form a large group of compounds with a complex and diverse chemical structures" - explained Dr. Magdalena Karamać from the Department of Chemical and Physical Properties of Food.
Tannins can be found in wine, tea, nuts. They are present in many berries such as blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, cranberries. Rich in tannins are also grapes, pomegranates, apples and legumes, particularly those with colour shells, like red beans, black beans, lentils. There are present also in buckwheat, dark chocolate and cocoa.
They play a very important role in wood, bark, roots, leaves, stems and fruits of plants. "They are a kind of plant defense mechanism against external threats, such as microbes, parasites, herbivores, and even adverse environmental conditions. Microbial proteins attached to tannins can not perform their functions and lead to the death of microbial cells" - described Dr. Karamać.
In the case of herbivores tannins act as "deterrents". Leaves and stems containing tannins siply taste bad to intruders. "The reason is a characteristic pungent, astringent taste, which is the result of tannins reacting with specific proteins contained in the animal saliva" - explained the scientist.
We can find out for ourselves how this works by drinking red wine, very strong tea and eating walnuts or unripe fruit.
"If animals feed on plants with very high tannin content despite the unpleasant taste, it can lead to the gastrointestinal tract disorders by blocking digestive enzymes. Such negative effects may also be experienced by humans" - said Dr Karamać.
In addition, tannins attached to iron and calcium present in the diet reduce their availability to the body, which may lead to anemia and osteoporosis. For these reasons, for several decades tannin were considered substances that should not be eaten.
However, products of tannins should not be avoided. Adverse effects occur only if you eat a lot of them. "With a normal, well-balanced diet rich in protein and micronutrients, the negative effects have no significant impact on our body" - assured the researcher.
In recent years, tannins began to reveal their good face to scientists. In recent studies, researchers demonstrate their beneficial effects. "It appears that these compounds may protect against different types of cancers, as well as slow down the rate of cancer cell division. They show antibacterial action and they are able to modify mouth and intestinal microflora, eliminating pathogenic organisms. Strong antioxidant action of tannins will neutralize free radicals that damage the basic structure of cells" - said Dr. Karamać.
The antioxidant action of tannins is important in extending the shelf life of food. An example is red wine that with tannins can mature for many years and not oxidise.
Researchers from the Department of Chemical and Physical Properties of Food PAS in Olsztyn isolate tannins from various products and determine how strongly they neutralize free radicals. "We are trying to explain the mechanisms of antioxidant action of tannins and the role of their interaction with metal ions and proteins in the process" - explained the scientist.
All tannins, regardless of the structure, have several common features. The most important is the ability to bind to proteins and form complexes, which are often insoluble. "This property has been practically used for centuries in the process of tanning leather. Due to the binding of tannins contained in plant extracts with collagen proteins of raw leather, leathers are flexible and do not decompose" - explained Dr. Karamać.
Tannins have also been used for a long time in the preparation of dyes. This process uses another important property - ability to bind to metal ions, resulting in the formation of coloured compounds. An example is the blue-black dye formed by the reaction of certain tannins with iron ions, used already in the Middle Ages to produce ink.
PAP - Science and Scholarship in Poland
ekr/ agt/ mrt/
tr. RL
Przed dodaniem komentarza prosimy o zapoznanie z Regulaminem forum serwisu Nauka w Polsce.