Ultra-Cold Ion-Atom Collisions in Quantum Regime
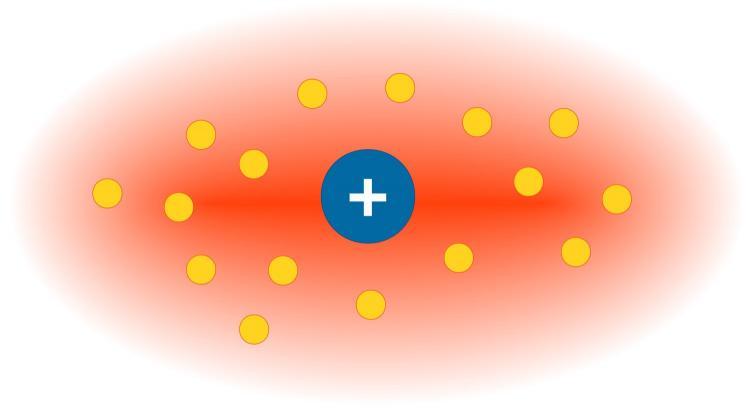 The diagram shows a single ion immersed in an ultra-cold gas of atoms. Source: Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw
The diagram shows a single ion immersed in an ultra-cold gas of atoms. Source: Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw
Dr. Michał Tomza from the Institute of Theoretical Physics of the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw, together with Dariusz Wiater, a PhD student of this faculty, and researchers from the University of Amsterdam, were the first to carry out time ultra-cold collisions in the quantum regime between a single ion and atoms. The results of their work were published in Nature Physics.
The Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw reminds in a press release that in recent years physicists have developed methods for creating extremely cold atoms and ions. These very cold particles have many applications, for example they can be used as components of quantum computers and very precise clocks. Mixtures of very cold atoms and ions could also be perfectly suitable for such applications, but, despite many efforts, so far it was only possible to cool individual types of particles separately to the required temperatures.
In the published article, Polish and Dutch scientists present combined theoretical and experimental results of research, in which such an ultra-cold mixture was created for the first time. This was possible thanks to the use of heavy ytterbium ions immersed in the ultra-cold gas of light lithium atoms. Theoretical analysis conducted by Dr. Tomza and Wiater confirmed that the quantum regime of ion-atom collisions was actually achieved. In addition, by building a complete theoretical model that reproduced the results of measurements, it was possible for the first time to determine the key collision parameters for describing the dynamics of the tested mixture. The results obtained were obtained after several years of cooperation between Dr. Tomza and the experimental group of Dr. Gerritsma from the University of Amsterdam.
`The results open up many new possibilities, such as the control of collisions between ions and atoms using a magnetic field. The resulting ultra-cold quantum mixture of ions and atoms can also serve as a new platform for quantum simulations of physics of many bodies. Another possibility may be a quantum computer based on ions cooled with ultra-cold atoms`, reports the Faculty of Physics of the University of Warsaw.
The research was supported by the National Science Centre (OPUS grant), the Foundation for Polish Science (First Team grant) and the European Research Council (Starting grant).
PAP - Science in Poland
agt/ kap/
tr. RL
Przed dodaniem komentarza prosimy o zapoznanie z Regulaminem forum serwisu Nauka w Polsce.