Expert: ICD in an envelope protects against infections
 Source: Department of Cardiology, Medical University of Warsaw
Source: Department of Cardiology, Medical University of Warsaw
Specialists at the Department of Cardiology, Medical University of Warsaw used a new method that reduces the risk of infection in patients, who receive implantable cardioverter-defibrillators - told PAP Dr. Marcin Grabowski, MD.
"Infections are among the most serious complications of the implantation or replacement of devices for electrotherapy of the heart. Very often, doctors have to remove the entire pacemaker system, which is more risky. Hence, doctors are looking for new methods to reduce the infection rate" - said Dr. Grabowski.
Cardioverter-defibrillator is the most effective method of preventing sudden cardiac death. It is implanted in patients who have survived an episode of sudden cardiac arrest and in primary prevention of myocardial infarction in patients in the high risk group.
According to the journal "Kardiologia Polska", in the years 2007-2010 the number of implanted cardioverter-defibrillators more than tripled in Poland - from approx. 2.5 thousand to 8 thousand per year. At the same time, the number of complications due to infection, despite the use of drugs that protect against infections, increased by 124 percent, and continues to increase faster than originally estimated.
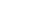
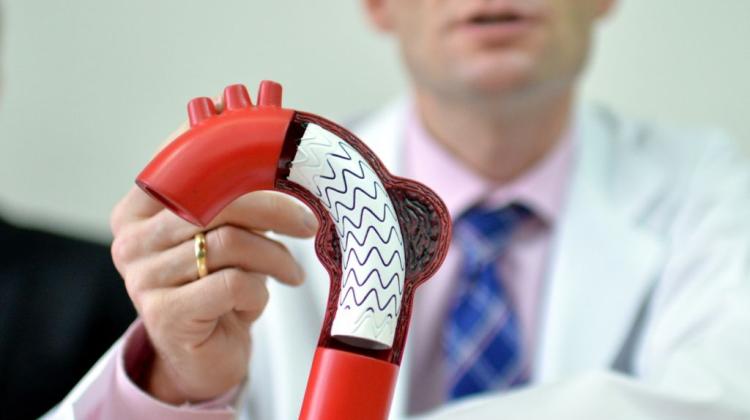
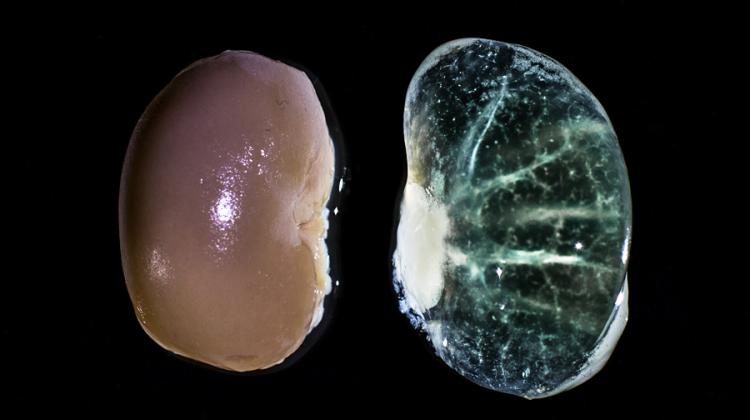
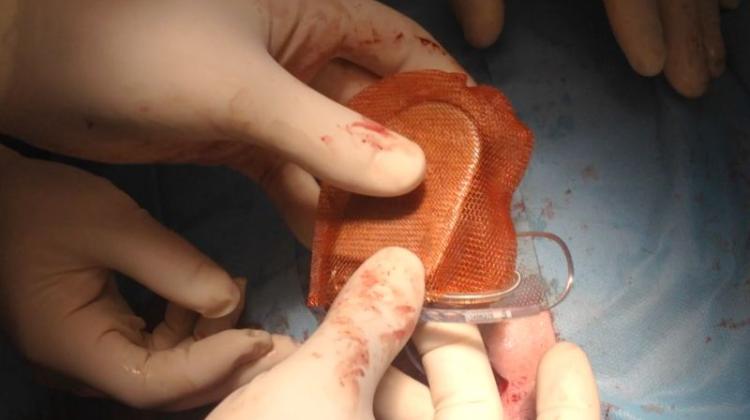
The new method used in the Department of Cardiology, Medical University of Warsaw, headed by Prof. Grzegorz Opolski, is to use so-called antibacterial envelope. It is a polypropylene mesh coated with a bioresorbable polymer that releases antibiotics, into which a cardioverter-defibrillator with resynchronization function is inserted. In addition, the envelope stabilizes the device and the electrodes, preventing their movement.
Dr. Grabowski emphasised that antibacterial envelope is used in patients at high risk of complications due to infection during treatments. "The results of international clinical trials recently presented at the CARDIOSTIM 2015 conference in Milan showed that the use of antimicrobial envelope allows to achieve up to 80-percent reduction in the risk of infection during replacement of implantable devices" - he added.
Few centimetre long cardioverter-defibrillator is implanted subcutaneously. At any time it can send an electrical pulse that interrupts life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias. The most dangerous types of arrhythmia include ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
The heart muscle contracts in an irregular way and loses its ability to pump blood. The brain and the entire body is hypoxic, the patient loses consciousness, and only 3 to 5 minutes remain to save him. Immediate action of cardioverter defibrillator can save the patient from sudden cardiac death.
PAP - Science and Scholarship in Poland
zbw/ agt/ mrt/
tr. RL
Przed dodaniem komentarza prosimy o zapoznanie z Regulaminem forum serwisu Nauka w Polsce.